It is a necessary to root Android device when recover data from internal memory. Let’s see how to root your phone.
What is rooting on Android?
Have you considered rooting your Android device? Many users tried this action in order to flash a custom ROM with a new version of Android system. Of course you may have read many articles about rooting but you do not have a clue what “rooting” actually means and why we should do it. This post will take you to going through the whole rooting thing in a quite easy way.
Simply put, rooting Android means getting “root” or admin right to your device so that you are able to access or edit system files which are not available to normal users. After an Android device is rooted, you or other apps that only work on rooted devices are able to access or change settings such as notification, recover lost data. The rooting process eliminates restrictions set by firmware, which is similar to those options like jailbreak iPhones and switch user account from normal user to administrator account on Windows computer.
Why do people root their Android device?
Rooting has been talked about too much and you probably should be aware of something about it, as you may already have an Android around you. Android is one of the most popular operating system used on smart mobile devices and you will be surprised by the reasons to root your phone.
Remove preinstalled crapware
When you buy in a brand new cellphone, you’ll find there are already many apps installed by default. However, you don’t need those preinstalled programs, and try to uninstall them by ways to remove other common apps. But those preinstalled apps can’t be removed! Those apps are battery-draining and space-wasting, and you have to get root access to your phone before you can totally remove them.
Perform Android data recovery
Many smartphone users have experience the problem of losing important data such as accidently delete photos, restore factory settings, etc. In that case, you’ll try to recover lost data from Android phone or tablet. But Android data recovery software can’t access storage media built in cellphone before the phone is rooted.
Flash a ROM for your smartphone
One of the features loved by Android users is that Android platform allow users to change version of Android on their devices. It also allows users to replace manufacturer-modded Android version with other another new and stock version. It takes quite long time for your manufacturer release a new system version after Google announces an Android update. Once rooted, your phone can be added new features through custom ROMs within short time.
Other reasons
Many people choose to root their phone so as to backup data automatically, block ads completely, install new system skins, unlock hidden features, install incompatible apps, etc.
How to root your android device?
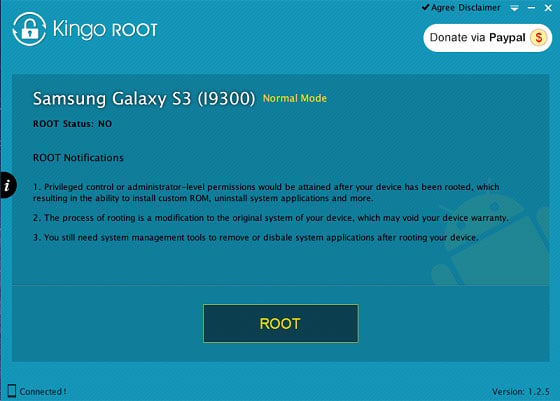
Rooting is usually a simple process, but there are no standard steps to root all devices. There are many rooting tools online and they make the rooting steps very easy. However, there is a vast of Android devices and no tool can support all of them. Thus you need to choose the rooting tool that supports your device. If the one you tried doesn’t work, then you need to do more search to find the rooting tool that works on your device.
Before rooting your phone, you need to connect phone to computer via USB cable and enable USB debugging mode, and make sure the battery level should be 50% at least.
Install root tool to your computer and launch it to recognize your phone, then you can follow the onscreen instruction to complete the operation.
What are the risks of rooting?
There are some potential disadvantages to root your device:
Void phones warranty: Some manufacturers doesn’t recommend users root phone, and it’ll void their warranty policies. In that case, if your phone gets any issues in the future, you’ll have to handle it by yourself.
Security risk: Malware has limited access to unrooted phone, but it can gain access to wider area of rooted phones, if you make a mistake if tapping on “Allow” requested by malware to deeper areas.
